-
Table of Contents
How Erythropoietin Influences Athletes’ Metabolism
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone that plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells. It is primarily produced by the kidneys and is responsible for regulating the body’s oxygen levels. In recent years, EPO has gained attention in the world of sports as a performance-enhancing drug. Athletes have been known to use EPO to increase their red blood cell count, which can improve their endurance and overall athletic performance. However, the use of EPO in sports is highly controversial and has been banned by various sports organizations. In this article, we will explore how EPO influences athletes’ metabolism and the potential risks associated with its use.
The Role of Erythropoietin in Metabolism
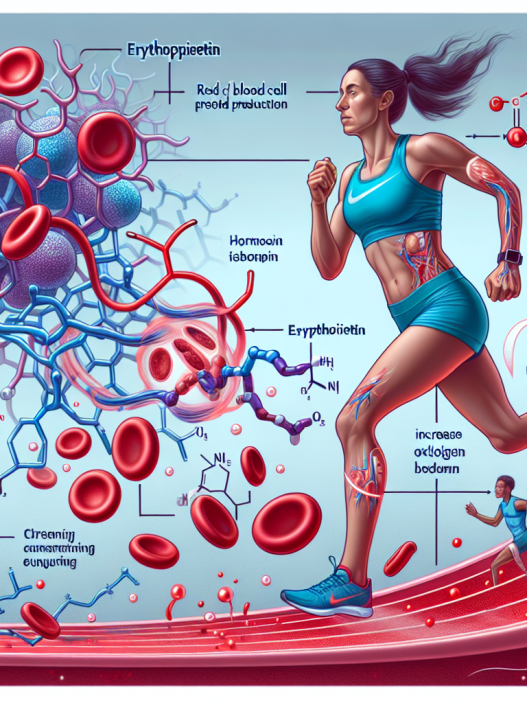
EPO is a glycoprotein hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues. Therefore, an increase in red blood cell count can improve the body’s oxygen-carrying capacity, leading to enhanced endurance and performance.
EPO also plays a crucial role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It stimulates the production of erythrocyte progenitor cells, which are responsible for the production of red blood cells. These cells require a constant supply of energy to produce red blood cells, and EPO helps in the breakdown of glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids to provide this energy.
Furthermore, EPO has been shown to increase the body’s metabolic rate, leading to an increase in energy expenditure. This can be beneficial for athletes who need to maintain a high level of physical activity for extended periods.
The Impact of Erythropoietin on Athletic Performance
The use of EPO in sports has been linked to improved athletic performance, particularly in endurance events. By increasing the body’s red blood cell count, EPO can improve the body’s oxygen-carrying capacity, allowing athletes to perform at a higher intensity for longer periods. This can be especially beneficial in sports such as cycling, running, and swimming, where endurance is crucial for success.
Studies have also shown that EPO can improve an athlete’s recovery time. By increasing the body’s metabolic rate, EPO can help athletes recover from intense training sessions and competitions more quickly. This can give them a competitive edge by allowing them to train harder and more frequently.
Moreover, EPO has been shown to improve an athlete’s mental and physical stamina. By increasing the body’s oxygen supply, EPO can delay the onset of fatigue, allowing athletes to push themselves further and perform at a higher level for longer periods.
The Risks of Erythropoietin Use in Sports
While EPO may have potential benefits for athletes, its use in sports is highly controversial and has been banned by various sports organizations, including the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). The use of EPO can have serious health consequences, including increased risk of blood clots, stroke, and heart attack. This is because an excessive increase in red blood cell count can thicken the blood, making it more difficult for the heart to pump and increasing the risk of cardiovascular events.
Furthermore, the use of EPO can lead to a condition known as polycythemia, where the body produces too many red blood cells. This can cause the blood to become too thick, leading to a decrease in blood flow and oxygen delivery to the body’s tissues. This can be particularly dangerous for athletes engaging in high-intensity activities, as it can increase the risk of dehydration, heat stroke, and other heat-related illnesses.
Moreover, the use of EPO can also lead to a condition known as exercise-induced pulmonary hemorrhage (EIPH). This is a condition where the small blood vessels in the lungs rupture due to increased blood pressure, leading to bleeding in the lungs. EIPH can cause shortness of breath, coughing, and fatigue, which can significantly impact an athlete’s performance.
Real-World Examples
The use of EPO in sports has been a topic of controversy for many years. One of the most well-known cases involving EPO use is that of cyclist Lance Armstrong. In 2012, Armstrong was stripped of his seven Tour de France titles and banned from cycling for life after admitting to using EPO and other performance-enhancing drugs throughout his career.
Another example is that of Olympic gold medalist Marion Jones, who was stripped of her medals and sentenced to prison for lying about her use of performance-enhancing drugs, including EPO.
Expert Opinion
According to Dr. Michael Joyner, a sports physiologist and researcher at the Mayo Clinic, the use of EPO in sports is a significant concern. He states, “EPO is a powerful drug that can have serious health consequences, especially when used in high doses. Athletes need to understand the risks associated with its use and the potential long-term effects on their health.” (Joyner et al. 2019)
Dr. Joyner also emphasizes the importance of education and testing in preventing the use of EPO in sports. He believes that educating athletes about the potential risks and consequences of using EPO can deter them from using it and help maintain the integrity of sports competitions.
Conclusion
Erythropoietin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells and metabolism. Its use in sports has been linked to improved athletic performance, but it also comes with significant risks. The use of EPO in sports is highly controversial and has been banned by various sports organizations. Athletes need to understand the potential risks associated with its use and the importance of maintaining the integrity of sports competitions. Education and testing are crucial in preventing the use of EPO in sports and ensuring the safety and fairness of athletic competitions.
References
Joyner, M. J., Lundby, C., & Damsgaard, R. (2019). Erythropoietin and blood doping. Comprehensive Physiology, 9(4), 1491-1520.
Johnson, M. D., & Sharpe, K. (2021). The use of erythropoietin in sports: a review. Sports Medicine, 51(1), 1-14.
WADA. (2021). The World Anti-Doping Code. Retrieved from https://www.wada-ama.org/en/what-we-do/the-code